4차 산업혁명 시대의 초·중등 교육을 위한 핵심 역량 연구
Copyright ⓒ 2022 The Digital Contents Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-CommercialLicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

초록
4차 산업혁명 시대의 새로운 기술적·사회적 조건에 적합한 인재 양성 교육 체제 구축이 매우 시급하고 중요하다. 이에 본 연구에서는 초·중등에서 4차 산업혁명 교육을 위한 핵심 역량이 무엇인지 고찰⋅제시한다. 우선 4차 산업혁명의 특징을 분석하고 이를 바탕으로 핵심 역량의 초안을 도출한다. 이어서 전문가 설문 조사⋅분석을 통해 핵심 역량의 수정안을 마련한다. 수정안에 대해 전문가 그룹과의 심층 대면 논의와 추가 심층 자문을 구한 후 핵심 역량의 최종안을 도출한다. 이와 같은 과정을 통해 본 연구진이 최종 도출한 핵심 역량은 지능 정보 역량, 융합·통찰 역량, 공존·공감 역량이다. 최종 도출한 역량은 설문 내용을 바탕으로 역량별 정의를 더욱 분명히 하고 범위를 명확히 설정하였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 핵심 역량은 4차 산업혁명 시대를 능동적⋅적극적으로 선도하는 인재를 양성하는 데 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
Abstract
In the era of the 4th industrial revolution (4IR), it is very urgent and important to establish an education system for nurturing talents suitable for new technological and social conditions. Therefore, this study intends to study and present the core competencies for the 4IR education in elementary and secondary schools. First, we analyze the characteristics of the 4IR and draw a draft of core competencies. Next, the modified version of the core competencies is made through a survey analysis of experts. After conducting in-depth face-to-face discussions with the expert group and additionally seeking in-depth advice from experts including pedagogical experts, we drive the final version of the core competencies. In this study, the core competencies finally obtained through a series of steps of deriving core competencies are intelligence information competency, convergence/insight competency, and coexistence/empathy competency. We expect that the derived core competencies for the 4IR education can be used as basic cornerstone to nurture talents who actively lead the era of the 4IR revolution.
Keywords:
Education in the 4IR, Core competencies, 2015 revised curriculum, Information subject, Talent cultivation키워드:
4차 산업혁명 교육, 핵심 역량, 2015 개정 교육과정, 정보 교과, 인재 양성Ⅰ. 서 론
다보스 포럼 설립자인 스위스 제네바대학교 교수 클라우스 슈밥은 ‘4차 산업혁명(The Fourth Industrial Revolution)’이라는 용어를 2016년 다보스 포럼에서 사용하였다. 4차 산업혁명이란 인공지능(AI, Artificial Intelligence), 사물인터넷(IoT, Internet of Things), 빅데이터(Big Data) 등이 주도하는 차세대 산업혁명을 말한다. 슈밥 교수는 4차 산업혁명 시대를 맞이하여 우리의 생활방식과 업무 방식, 그리고 다른 사람과 관계를 맺는 방식까지 완전히 바뀌게 될 것으로 전망했다[1]. 3차 산업혁명까지는 산술급수적으로 전개되었으나, 4차 산업혁명은 기하급수적으로 전개되며 사회 전반에 걸친 큰 변화를 요구하고 있다.
4차 산업혁명의 진전, 특히 인공지능 발전의 영향으로 교육 분야 역시 광범위한 대변혁의 과제 앞에 놓여 있다. 이는 인공지능과 공존해야 하는 미래 사회의 구성원들에게 지식의 단순 습득이 아니라 4차 산업혁명의 본질에 대한 이해에 바탕을 둔 비판적·창의적 사고 역량이 요구되기 때문이다. 그런 역량을 효과적으로 평가ㆍ함양하기 위한 교육 패러다임의 전환은 4차 산업혁명 사회의 시대적 요청이다. 4차 산업혁명 교육은 그런 요청에 부응하도록 설계ㆍ준비되어야 한다.
현재 초·중등 교육 현장에 적용되고 있는 2015 개정 교육과정[2]은 4차 산업혁명이 본격적으로 시작된 2016년 이전에 마련되었기에 4차 산업혁명 시대의 요구 사항에 충분히 부응하지 못하고 있다. 또한, 초·중등 교육과정 상에서 국가에서 핵심 역량을 제시하고 있기 때문에 초·중등 핵심역량에 대한 연구가 거의 없다. 그러므로 급변하는 기술이나 사회 변화를 반영한 체계적이고 심층적인 핵심 역량에 대한 연구를 도출하여 교육의 다양성과 명확성을 제고할 필요가 있다.
현재 2015 개정 교육과정을 개선한 2022 개정 교육과정이 만들어지고 있다[3]. 2022 개정 교육과정에서는 4차 산업혁명 시대에 요구되는 인재상과 역량을 일부 반영할 것으로 예상된다. 하지만 4차 산업혁명 뿐 만 아니라 다양한 요소를 모두 반영해야 하는 국가 교육과정상 4차 산업혁명에만 초점을 맞춘 핵심 역량을 제시하기 어렵다.
따라서 4차 산업혁명으로 인해 야기되는 사회 변화의 폭이나 깊이, 속도가 엄청난 만큼, 미래 핵심 역량을 효과적으로 함양시키기 위한 4차 산업혁명 교육 체제의 구축ㆍ운영은 매우 시급하고 중차대한 일이다. 여기에서 놓치지 말아야 할 사항은 4차 산업혁명 교육의 중심에 초·중등 교육을 둠으로써 교육의 실효성을 높일 필요가 있고, 4차 산업혁명 교육을 통해 제고시켜야 할 핵심 역량을 제대로 도출ㆍ정의함으로써 교육의 방향을 올바르게 설정해야 한다는 것이다.
이에 본 연구는 4차 산업혁명에 따른 변화의 본질을 심층적으로 이해하고, 그것을 바탕으로 4차 산업혁명 시대를 선도하며, 발생 가능한 다양한 상황에 효과적으로 대처할 수 있는 인재를 양성하기 위해 설정해야 할 초·중등 4차 산업혁명 교육의 핵심 역량을 고찰ㆍ도출ㆍ정의하고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 핵심 역량 고찰과 도출 과정
2-1 기존 핵심 역량 고찰
현재 초·중등 교육은 2015 개정 교육과정에 바탕을 두고 있다. 2015 개정 교육 과정에는 학생들이 갖추어야 할 여섯 가지 핵심 역량으로 자기 관리 역량, 지식 정보처리 역량, 창의적 사고 역량, 심미적 감성 역량, 의사소통 역량, 공동체 역량을 제시했다[2]. 이들 역량은 4차 산업혁명이 본격적으로 시작된 2016년 이전에 도출⋅정의된 것이다. 그로 인해 4차 산업혁명 시대의 요구 사항이 충분히 반영되어 있지 않다. 또한, 하위 역량을 구체적으로 정의하지 않고 있기 때문에 세분화된 교육 목표를 설정하고 달성하는 데 어려움이 있다.
4차 산업혁명 교육과 가장 관련성이 깊은 교과가 정보 교과이다. 2015 개정 교육과정상의 정보 교과에서는 핵심 역량으로 정보 문화 소양 역량, 컴퓨팅 사고력, 협력적 문제해결력을 제시하고 있다[4]. 또한 정보 문화 소양 역량에는 정보윤리의식, 정보보호능력, 정보기술 활용능력을, 컴퓨팅 사고력 역량에는 추상화 능력, 자동화 능력, 창의·융합 능력을, 협력적 문제해결력에는 역량에는 협력적 컴퓨팅 사고력, 디지털 의사소통능력, 공유와 협업 능력을 하위 역량으로 설정하고 있다. 이와 관련하여 2022 교육과정 개편을 앞두고 이전까지의 정보과 교육과정을 고찰하는 연구가 있다[5]. 이 연구에서는 2015 개정 교육과정에서 제시하지 않았던 인재상을 명확히 정의하고 정보과 역량을 컴퓨팅 사고 역량, 네트워크 역량, 디지털 감성 역량으로 설정하여 기존 정보 교과와 조금 다르게 제시하고 있다. 역량 관련하여 2015 정보과 개정 교육과정과 비교해 보면, 인공지능 등 4차 산업혁명 기술의 발달에 따라 정보문화소양 역량 대신에 디지털 감성 역량을 새롭게 도입한 것이 특징적이다.
4차 산업혁명 논의가 시작된 세계경제포럼은 21세기에 필요한 역량 세 가지를 제시하고 열여섯 가지 핵심 기술을 제안하였다[6]. 후자의 핵심 기술 열여섯 가지는 전자의 세 가지 역량으로 분류되는데, 여기에는 기본 기술군(Foundational skills), 역량군(Competencies), 인성 자질군(Character Qualities)이 있다. 기본 기술군은 문해, 산술 능력, 과학 문해, ICT(Information and Communications Technology) 문해, 재정 문해, 문화 및 시민 문해 역량 등으로 구성되고, 역량군에는 비판적 사고 및 문제해결, 창의성, 의사소통, 협력 역량 등이 포함되며, 인성 자질군에는 호기심, 주도성, 일관성과 도전 정신, 적응력, 리더십, 과학 및 문화 역량 등이 속해 있다.
4차 산업혁명 시대의 디지털 역량에 관한 연구에서는 4차 산업혁명 시대에 요구되는 디지털 역량을 정의하고 디지털 역량에 어떤 요소들이 포함되어야 하는지를 고찰하였다. 특히 디지털 역량에 대한 프레임워크를 제공하고 있다[7]. 또한, 디지털 시민역량에 관하여 살펴본 연구가 있었다. 이 연구에서는 디지털 시민 역량의 개념과 특성을 정리하고 현행 교육과정에서 디지털 시민역량을 강화할 수 있도록 교육 정책의 현황과 문제점을 분석하였다[8].
유아 교육에서 4차 산업혁명 시대의 핵심 역량을 향상시키기 위한 연구가 있었다[9]. 또한, 4차 산업혁명 시대의 유아 핵심 역량으로 창의적 문제해결 역량, 윤리적 인성 역량, 협업 및 소통역량, 자기 주도적 역량, 테크놀로지 활용 능력, 신체역량으로 구성한 연구가 있었다[10]. 두 연구는 초·중등이 아니라 유아 교육 방향에 대한 연구로 본 연구와 차이점이 있다.
4차 산업혁명 시대의 전문대학생들이 갖춰야할 핵심 역량을 도출하여 제시한 연구가 있었다[11]. 이 연구에서는 전문대학생들이 갖춰야 할 핵심역량으로‘의사소통능력’, ‘문제해결능력’, ‘정보처리능력’, ‘대인관계능력’, ‘자기관리능력’을 제시하고 있다. 또한, 대학에서 교양 교과목 컴퓨팅 사고력 교과목과 연계한 학습 지원 비교과 프로그램이 대학생의 핵심 역량 미치는 효과를 분석한 연구가 있었다[12].
이외에도 인공지능 융합 교육을 위한 교원의 역량에 대한 연구가 있었다[13][14]. 이 연구에서는 교원의 융합교육 역량으로 지식 연결 역량과 교육과정 재구성 역량을 도출하였다.
유럽의 경우 초·중등 교육에서의 핵심 역량을 모국어 의사소통 역량, 외국어 의사소통 역량, 수학적 역량과 과학기술 기초 역량, 디지털 역량, 사회 및 시민 역량, 배우는 방법을 배우는 역량, 자기주도 및 모험 역량, 문화적 감수성과 표현 역량 등 8개 역량을 제시하고 있다[15]. 프랑스의 경우 유럽에서 제시한 핵심 역량을 바탕으로 초·중등 교육에서의 핵심 역량으로 프랑스어 숙달 역량, 외국어 사용 역량, 수학 및 과학기술 소양, 정보와 통신 기술 숙달, 인문학적 소양, 사회적 및 시민 역량, 자율성과 진취성 등 7개 핵심 역량을 제시하고 있다[15].
핵심 역량에 대한 기존 논의를 종합적ㆍ분석적으로 정리하면 다음과 같다. 첫째, 역량을 지칭하는 용어들은 상이하지만 공통적인 역량으로 분류될 수 있는 부분이 많았다. 예를 들면, 기술 관련 역량, 사회적 역량, 창의 융합 역량 등에 해당하는 역량이 공통적으로 많이 들어 있었다. 둘째, 핵심 역량은 국가나 회사 등에 따라 요구되는 역량에 차별성이 있었다. 예를 들면, 구글은 회사의 특성을 살린 역량이 들어 있고, 유럽이나 프랑스는 유럽 공동체의 특성을 반영한 외국어 역량 등이 포함되어 있었다.
Ⅲ. 핵심 역량 고찰과 도출 과정
3-1 핵심 역량 초안
4차 산업혁명의 대표적 특징으로 대두되는 초지능(Hyper Intelligence)⋅초융합(Hyper Convergence)⋅초연결(Hyper Connectivity)은 컴퓨팅이 4차 산업혁명의 핵심 요소로 작용하고 있기 때문에 두드러지게 나타나는 특성들이다. 이들 특성 각각이 컴퓨팅과 어떻게 연계되어 있는지 간략히 정리하면 다음과 같다.
- ∙ 초지능 : 학습 능력, 추론 능력 등을 갖춘 컴퓨팅 시스템을 구현ㆍ구축ㆍ적용해 교육, 문화, 사회, 경제, 산업 전반에 큰 변화가 일어나고 있음.
- ∙ 초융합 : 컴퓨팅 이론 및 기술이 급격히 발전하면서 컴퓨팅 기반의 디지털 기술을 매개로 이전에는 상상조차 할 수 없었던 지식이나 기술의 융합이 촉진되고 있음.
- ∙ 초연결 : 컴퓨팅 및 관련 기술의 급격한 발전으로 인간과 인간, 인간과 사물, 사물과 사물 간 연결의 범위가 급속히 확대되고 있으며, 컴퓨팅 기술의 유연성을 바탕으로 상호작용 양식의 제한이나 상호 작용의 시공간적 제약이 거의 없어져 가고 있음.
따라서 초지능ㆍ초융합ㆍ초연결의 바탕이 되는 컴퓨팅의 본질이 4차 산업혁명에 어떻게 작용하고 있는지 올바로 알아야, 급격하고 전 방위적인 변화를 보다 깊이 이해하고 효과적으로 적응ㆍ선도할 수 있게 된다. 이를 바탕으로 본 연구에서 1차로 도출한 4차 산업혁명 시대에 필요한 핵심 역량은 지능 정보 역량, 디지털 융합 역량, 공감 혁신 역량이다.
- ∙ 지능 정보 역량 : 컴퓨팅에 대한 본질적 이해를 바탕으로, 컴퓨터의 처리 능력을 적용해 복잡하고 규모가 큰 문제를 효과적으로 해결할 수 있는 역량. ‘초지능’을 제어ㆍ관리하기 위해 요구되는 역량으로, 컴퓨팅의 본질에 대한 심층적 이해 및 적용에 주안점을 둠.
- ∙ 디지털 융합 역량 : 지식에 대한 깊은 통찰을 바탕으로, 디지털 관점에서 관련 지식을 융합·적용할 수 있는 역량. ‘초융합’과 관련해 능동적으로 대응ㆍ선도하기 위한 역량으로, 컴퓨팅에 기반을 둔 제반 지식의 접목ㆍ융합에 주안점을 둠.
- ∙ 공감 혁신 역량 : 인간ㆍ기술ㆍ자연이 공존하는 계에서 공감ㆍ소통ㆍ협력하고, 자기 혁신과 성찰을 통해 아름다움과 가치를 추구ㆍ향유하는 역량. ‘초연결’에 대해 올바로 이해ㆍ대응하기 위한 역량으로, 서로 함께 지속 발전하는 공동체에 초점을 맞춤.
이들 핵심 역량과 그 하위 역량에 대한 본 연구에서의 정의 내용이 <Table 1>에 제시되어 있다. <Table 1>에 첫 번째 핵심 역량으로 제시된 지능 정보 역량은 4차 산업혁명의 특징 중 하나인 ‘초지능’과 관련해 설정된 역량이다. 4차 산업혁명 시대는 자연 사물, 기기 등 제반 개체들이 컴퓨팅 기술과 결합되어 지능화되는 시대이다. 이들을 효과적으로 활용하는 방법은 그 계산(처리) 능력이 우리가 원하는 대로 작동하게 만드는 것이다. 그렇게 만들 수 있으면 해당 개체의 계산 능력은 우리 개개인의 것이 된다. 그렇게 하려면 관련 개체들이 어떤 계산 능력을 가지고 어떻게 작동하는지 파악할 수 있어야 하고, 우리가 원하는 활동을 그들의 상호작용으로 설계해 낼 수 있어야 한다. 또한 우리가 설계한 방식대로 해당 개체들이 작동하게 만들 수 있어야 하고, 우리가 부딪힌 문제를 어떻게 해결할 수 있는지 그 해결책을 찾아낼 수 있어야 한다. 이점을 고려해 설정된 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량이 컴퓨팅 사고력, 프로그래밍 역량, 문제해결 역량이다.
- ∙ 컴퓨팅 사고력 : 주변 세계를 고유의 계산 활동을 수행하고 있는 수많은 사물(계산의 주체) 간의 상호작용으로 인식ㆍ해석할 수 있는 역량과 다양한 계산 활동들을 분석ㆍ평가하고 좋은 계산 활동을 설계하려 할 때 요구되는 사고 역량
- ∙ 프로그래밍 역량 : 프로그래밍은 우리가 구상한 계산 활동을 특정 컴퓨터가 수행하게 만드는 활동이므로, 프로그래밍 역량은 찾아낸 해결책을 특정 컴퓨터가 이해하고 수행할 수 있게 표현ㆍ설명할 수 있는 역량
- ∙ 문제해결 역량 : 실세계 문제에 대한 문제해결 활동의 주체가 나 자신일 때뿐만 아니라 다른 사람 혹은 컴퓨팅 기기일 때 적용하기에 알맞은 해결책을 도출해 내는 역량
<Table 1>에 두 번째 핵심 역량으로 제시된 디지털 융합 역량은 4차 산업혁명의 특징 중 하나인 ‘초융합’과 관련해 설정된 역량이다. 4차 산업혁명 시대는 이미 존재하는 기술들과 이미 알고 있는 지식들, 그것들의 본질을 통찰하고 새롭게 해석하고 결합하여 새로운 것이 창조되고 막대한 가치가 창출되는 시대이다. 모든 사물과 지식을 디지털화함으로써 전혀 다른 영역의 것들을 함께 다룰 수 있고, 보다 쉽게 결합시킬 수 있게 된다. 컴퓨팅 이론이나 기술, 컴퓨팅 기기의 계산 능력을 매개로 유연하게 엮을 수 있고 함께 작용하게 만들 수 있다. 디지털 융합 역량의 하위 역량으로 통찰적 학습 역량, SWㆍAI 융합 역량, 디지털 리터러시를 설정한 배경은 다음과 같다.
- ∙ 통찰적 학습 역량 : 진정한 융합은 관련 지식에 대한 통찰을 요구한다. 관련 지식의 본질을 깊이 이해할 때 해당 지식들에 대한 물리적 융합을 넘어 화학적 융합이 가능해진다. 따라서 지식의 본질을 통찰할 수 있는 학습 역량을 키울 수 있게 초·중등 학생들을 교육해야 한다.
- ∙ SWㆍAI 융합 역량 : 컴퓨팅(SW, SoftwareㆍAI, Artificial Intelligence)은 다양한 분야의 지식들을 효과적으로 수용해 융합할 수 있게 해 준다. 물론 거기에는 SWㆍAI의 핵심 개념이나 원리, 기술 등에 대한 깊은 이해가 요구된다. 그것이 바탕이 될 때 한 교과의 지식이 반영된 컴퓨팅 기반의 문제 해결책을 보다 쉽게 구상할 수 있게 되고, 다수 교과의 지식을 융합한 컴퓨팅 기반의 문제 해결책을 보다 효과적으로 구상할 수 있게 된다.
- ∙ 디지털 리터러시 : 디지털 뉴미디어 기술과 콘텐츠를 주체적으로 수용할 수 있어야 하며, 제반 정보를 디지털 콘텐츠로 만들어 최적의 디지털 미디어를 매개로 저장ㆍ관리할 수 있어야 한다.
<Table 1>에 세 번째 핵심 역량으로 제시된 공감 혁신 역량은 4차 산업혁명의 특징 중 하나인 ‘연결’과 관련해 설정된 역량이다. 4차 산업혁명 시대에는 다양한 요소들이 서로 연결되어 상호작용하기에 서로 공존해야 하는 시대이다. 사람이 그렇고, 자연이 그렇고, 사물들, 인공지능 시스템들이 그렇다. 그들의 존재를 받아들이고 서로 존중하고 살아가야 하며, 서로의 다양성을 인정하고 공감하며 살아가야 한다. 관계 속에서 심미적 가치를 추구ㆍ향유하며 살아갈 수 있어야 한다. 늘 새로운 것들과 연결되어 새로운 관계가 형성되고 거기에 적응하고 그런 것들을 올바로 경쟁력 있게 다루려면 새롭게 배워야 하고 스스로를 지속적으로 혁신ㆍ발전시켜 가야 한다. 공감 혁신 역량의 하위 역량으로 심미적 감수성, 공존 공감 역량, 자기 혁신 역량을 설정한 배경은 다음과 같다.
- ∙ 심미적 감수성 : 4차 산업혁명 사회는 현실 세계와 가상 세계가 병존하는 사회이다. 다양한 사회 현상과 변화 속에서 그런 변화에 어떻게 반응하는 것이 바람직한지, 무엇이 올바르고 가치 있는 것인지 제대로 판단하고 능동적으로 참여할 수 있어야 한다.
- ∙ 공존 공감 역량 : 4차 산업 혁명 사회는 제반 요소들이 연결되어 상호 영향을 주고받는 사회이다. 따라서 인간ㆍ환경ㆍ문화의 고유성 및 다양성에 대한 공감적 이해를 바탕으로 상호 협력ㆍ공존할 수 있는 역량이 필요하다.
- ∙ 자기 혁신 역량 : 4차 산업혁명 사회는 제반 요소 간 연결이 확장되면서 연결 구조의 규모도, 연결 관계의 복잡성도 지속적으로 커지는 사회이다. 따라서 지속적으로 자신을 성찰ㆍ발전시켜 가며 사회 변화에 능동적으로 대처하고 선도할 수 있는 역량이 필요하다.
본 연구진이 핵심 역량 도출의 기본 전제로 설정한 사항을 다시 한 번 간략히 정리하면 다음과 같다.
- ∙ 컴퓨팅에 대한 본질적 이해가 바탕이 될 때, 4차 산업혁명 시대의 핵심 요소인 초지능ㆍ초융합ㆍ초연결을 올바로 이해하고 이에 따라 급변하는 사회에 대한 대응 능력을 갖출 수 있다.
- ∙ 관련 지식에 대한 통찰적 이해가 바탕이 될 때 진정한 융합이 가능하다.
- ∙ 컴퓨팅(SWㆍAI)은 융합의 훌륭한 도구이자 촉진제이다.
- ∙ 제반 현상에 대해 올바로 이해ㆍ반응하려면 관련 요소들을 컴퓨팅의 관점에서 바라보고 다루어야 한다.
3-2 적절성 분석
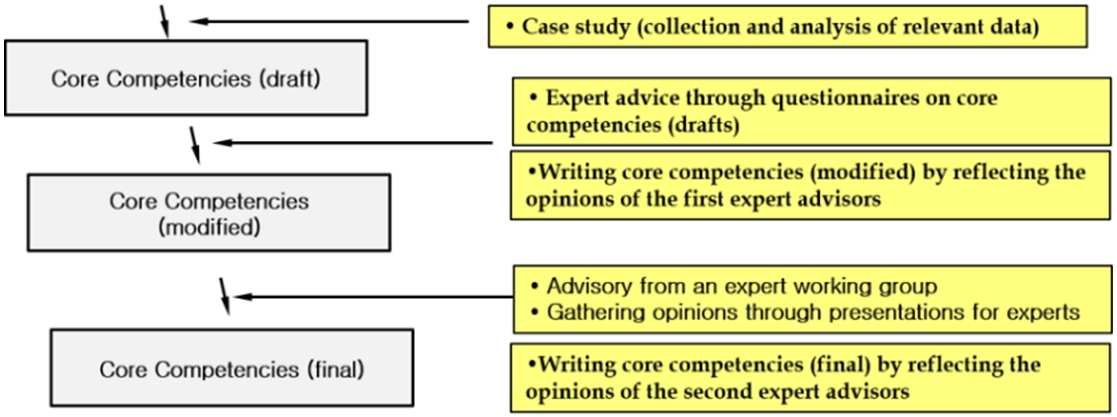
본 연구에서 선정한 핵심 역량의 타당성을 확인하기 위하여 전문가를 대상으로 설문 응답을 진행하였다. 설문에 참여한 인원은 대학 교수 16명, 교육청 관계자 2명, 초·중등학교 교사 4명으로 총 22명이었다. 응답을 ICT 관련 분야 종사자와 그 이외 분야 종사자로 구분하였다. ICT 관련 분야에 종사하고 있는 인원은 기관별로 SW 관련 학과 교수 11명, 교육청 미래인재교육과 1명, 초·중등학교 정보ㆍ컴퓨터 교사 4명으로 구성되었다.
설문 응답자 중 ICT 관련 분야 16명과 그 외 분야 6명을 대상으로 핵심 역량의 타당성 및 하위 역량의 타당성에 대하여 기술 통계를 작성하였다.
이에 대한 결과는 <Table 2>와 같다.
<Table 2>에서 보는 것처럼, 설문 응답 결과에서 전체적으로 긍정의 응답을 보였다. 핵심 역량의 구성과 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량의 적절성은 긍정 응답이 꽤 높게 나왔지만 상대적으로 ‘공감 혁신 역량’의 적절성을 묻는 문항에서 가장 낮은 긍정 비율이 나타났다. 이에 관한 해당 문항에서‘적절하지 않다’의 서술형 의견은 다음과 같다.
“심미적 감수성이라는 용어가 쉽게 다가오지 않음”, “핵심 역량의 명칭이 하위 역량을 포괄하기에 한계가 있음”, “감수성은 공존 공감 역량의 한 부분으로 생각됨”
이러한 응답이 나온 이유는 ‘공감 혁신 역량’에 대해 보는 관점에 따라 다양한 해석이 가능하기 때문으로 보인다. 이 외에도 다양한 서술식 의견이 있었는데 이에 대한 의견과 반영은 다음 장에서 기술한다.
Ⅳ. 핵심 역량 수정 및 최종안
4-1 핵심 역량 수정안
본 연구에서는 핵심 역량 초안에 대한 전문가 자문을 거쳐 <Table 3>에 제시된 핵심 역량 수정안을 만들었다. 핵심 역량 초안 내용 중 수정⋅보완된 부분은 다음과 같다. 첫째, ‘공감 혁신 역량’이라 명명된 역량 이름에 가운뎃점을 추가하여 ‘공감⋅혁신 역량’으로 수정하였다. 이렇게 함으로써 ‘공감⋅혁신 역량’이 ‘공감’과 ‘혁신’ 각각의 고유 의미 모두가 포함된 역량임을 명확히 하였다. 둘째, 하위 역량 중 ‘공존 공감 역량’ 역시 ‘공존’과 ‘공감’ 두 단어의 독자적 의미를 포괄하도록 ‘공존⋅공감 역량’으로 수정하였다. 셋째, ‘공존⋅공감 역량’이 다른 하위 역량과 어떻게 구별되는 지나, 4차 산업혁명과 어떤 연관성이 있는지를 더욱 명확히 나타내기 위해, ‘공존⋅공감 역량’의 정의를 일부 보완해 해당 역량이 온⋅오프라인 환경 전반을 포괄하고 있는 역량임을 명시하였다.
<Table 3>의 핵심 역량 수정안이 <Table 1>에 제시된 핵심 역량 초안을 수정ㆍ보완한 것이지만 전문가 의견 반영의 폭이 그리 크지 않음을 알 수 있는데, 그 이유는 다음과 같다. 첫째, 핵심 역량(초안)에 대해 교수, 교사 등 4차 산업혁명 관련 전문가들로부터 설문 조사를 통해 의견을 수렴한 결과 핵심 역량 초안이 ‘부적절하다’는 의견은 3~4명의 소수 의견이었으며, 대다수 전문가들은 핵심 역량 초안을 긍정적으로 평가하였다. 따라서 추후 또 다른 전문가 그룹과의 심층 논의를 상정하여 핵심 역량 초안의 기본 틀을 유지하는 것이 바람직하다고 판단하였다. 둘째, 핵심 역량의 수정안은 핵심 역량 최종안 마련을 위한 한시적 중간 안일뿐임을 고려한 판단이었다. 핵심 역량 최종안은 설문 조사 방식이 아니라 전문가로 구성된 위원회와 발표 토론, 그리고 전문가 대상의 심층 자문 등 종합적 보완 과정을 통해 확정되는 것으로 기획하였다. 핵심 역량 최종안의 실제 도출 과정은 다음 절에 구체적으로 기술되어 있다. 셋째, 문제해결 역량의 범위가 상위 핵심 역량보다 넓다는 의견이 있었지만, 이 의견을 핵심 역량(초안)에 제시된 문제해결 역량이 ‘컴퓨팅 기반’의 해결책 도출과 관련된 역량으로 정의되어 있음을 간과해 제시된 것이라 판단하고, 추후 논의 과정에서 관련 요구가 지속될 경우 수정ㆍ보완하기로 결정하였기 때문이다. 넷째, 지능 정보 역량과 디지털 융합 역량의 중첩이나, 심미적 감수성과 공존 공감 역량의 중첩에 대한 의견이 있었지만, 연구진 자체 논의 결과 각 역량의 정의를 통해 어느 정도 구분이 되고 있다고 판단해 관련 수정 작업을 유보하였기 때문이다. 다만, 이 부분에 대해서도 추후 논의를 거치면서 관련 요구가 지속될 경우 수정ㆍ보완하기로 하였다.
4-2 핵심 역량 최종안
초안과 수정안으로 도출ㆍ제시된 핵심 역량에 대한 전문가 검토ㆍ자문 의견의 대다수는, 핵심 역량 각각이 본질적으로 어떤 역량을 의미하는지, 해당 역량을 키우면 어떤 일들을 잘 할 수 있게 되는지 설명이 미흡하다는 의견들로 간주될 수 있다. 그 이유는 컴퓨팅 사고력, 프로그래밍, 디지털 융합 등은 컴퓨팅 분야에서 더 깊이 체계적으로 다루어지는 용어이지만, 일상의 활동뿐만 아니라 학문 분야 전반에서 일어나고 있는 활동과 연계된 용어이기 때문이다. 다음은 그와 관련해 간단히 제시할 수 있는 예시이다.
- ∙ 컴퓨팅 사고력 : 특정 방식으로 상호작용하는 사람들 간에 어떤 문제가 발생할 수 있는지, 해당 문제를 어떤 방법으로 해결하는 것이 효과적인지 구상할 때 요구되는 사고 능력
- ∙ 프로그래밍 역량 : 누군가가 특정 방식으로 행동하도록 행동 방식을 제대로 설명하거나 효과적으로 가르칠 수 있는 능력
- ∙ 디지털 융합 역량 : 관련 활동이 정확히 재현될 수 있도록 지식 융합의 산출물을 도출ㆍ적용할 수 있는 역량
따라서 본 연구진은 <Table 3>에 제시된 핵심 역량 중 일부를 보다 일반화된 용어로 명명하거나 그 정의 내용을 보다 명확히 설명ㆍ정의하는 방식으로 수렴 의견을 반영하였다. 해당 작업의 결과로 도출ㆍ정리된 핵심 역량 최종안이 <Table 4>에 제시되어 있다. ‘지능 정보 역량, 컴퓨팅 사고력, 프로그래밍 역량 등에 대한 정의를 정보 처리’의 관점에서 재기술한 것도 그런 맥락에서 이루어진 것이다. 그들 역량과 ‘정보 처리’와의 관계를 구체적으로 제시함으로써, 해당 역량이 상태 변화가 수반된 우리 일상의 제반 활동 수행 능력 제고에 유익이 되는 역량임을 보다 명확히 한 것이다.
<Table 3>과 <Table 4>를 대비시켜 보면 문제해결 역량, 디지털 융합 역량, 자기 혁신 역량의 세 가지 역량의 명칭이 바뀐 것을 알 수 있는데, 이는 다음을 고려한 것이다.
- ∙ 문제해결 역량을 데이터 리터러시로 변경 : 데이터 리터러시는 인공지능이나 빅데이터 관련 문제 등과 같이, 데이터의 특성이나 데이터 내재 의미에 대한 직관력, 데이터를 적절히 해석⋅수집⋅정제⋅생성해 보다 효과적으로 문제를 해결할 수 있는 데이터 역량을 의미하며, 지능 정보 역량과의 상⋅하위 관계를 명확히 하는 데 적합함. 더욱이 지능 정보 역량의 또 다른 하위 역량인 컴퓨팅 사고력이나 프로그래밍 역량과 범주 구분도 더 명확히 할 수 있음.
- ∙ 디지털 융합 역량을 융합ㆍ통찰 역량으로 변경 : 융합ㆍ통찰 역량은 디지털 융합 역량보다 폭넓게 융합 관련 능력을 포괄하는 명칭이며, 진정한 ‘융합’이 깊은 ‘통찰’과 관련되어 있음을 명확히 나타냄.
- ∙ 자기 혁신 역량을 성찰ㆍ혁신 역량으로 변경 : 성찰ㆍ혁신 역량이 자기 혁신 역량보다 성찰을 강조하는 명칭이며, 실천적 성찰을 보다 명확히 나타냄.
Ⅴ. 핵심 역량 비교 분석
5-1 2015 개정 교육과정과의 비교 분석
앞서 핵심 역량 고찰에서 알아본 2015 개정 교육과정에서의 핵심 역량과 본 연구의 핵심 역량을 비교 분석하면 <Table 5> 같다. 또한, 2015 개정 교육과정에서의 핵심 역량과 본 연구의 핵심 역량을 대비시켜 각 역량의 특징과 역량 간 관계를 설명하고 있다.
디지털 융합 역량의 명칭을 융합ㆍ통찰 역량으로 변경하면서 그 하위 역량인 통찰적 학습 역량과 SWㆍAI 융합 역량의 정의를 다음을 고려해 일부 보완하였다.
- ∙ 통찰적 학습 역량 : 통찰적 학습 역량이 ‘어떤’ 학습 역량인지가 명확히 드러나도록 원 정의를 보완함.
- ∙ SWㆍAI 융합 역량 : ‘통찰’의 의미가 내포되도록 원 정의를 보완함.
<Table 6>은 <Table 4>에 정의⋅제시된 역량들에 대한 이해도를 높이기 위해 각 역량을 4차 산업혁명 교육의 핵심 역량으로 설정한 배경이 무엇인지, 핵심 역량의 하위 역량들이 어떤 배경에서 그렇게 설정되었는지 등을 보다 다양한 관점에서 설명했다.
5-2 2015 개정 정보교과와의 비교 분석
4차 산업혁명 교육 핵심 역량과 2015 개정 정보 교과의 핵심 역량[16]을 대비하면 <Table 7>로 정리할 수 있다. 여기에서 유의해야 할 점은 전자와 후자가 서로 다른 관점에서 도출된 역량이라는 것이다. 전자의 초점은 시대가 요구하는 역량 중에 학교 교육 시스템 전반을 통해 집중 함양해야 할 역량이 무엇인지에 있었고, 후자의 초점은 시대가 필요로 하는 역량 중에 어떤 역량을 정보 교과를 통해 키워 줄 수 있는지에 맞추어졌다. 또 한 가지 유의할 점은 전자의 역량 중에 4차 산업혁명의 핵심 분야인 컴퓨팅과 밀접하게 관련되어 있는 지능 정보 역량이 정보 교과의 주도적 역할 하에 키워지도록 설정된 역량이라는 것이다.

Comparison of 2015 revised curriculum information subject core competencies and our core competencies(final)
<Table 7>에 제시된 바, 컴퓨팅 사고력을 전자와 후자가 서로 다르게 다루고 있는 것도 앞서 기술한 유의 사항과 관련지어 이해할 필요가 있다. 전자의 경우 국어, 영어, 수학, 과학, 사회, 정보 등 전 교과의 관점에서 컴퓨팅 사고력을 계산 개념에 기초해 세상을 이해하고 다루기 위해 필요한 기본 역량으로 좁게 해석해 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량으로 설정하고 있는 것이고, 후자의 경우 정보 교과의 관점에서 컴퓨팅 사고력을 프로그래밍 능력이나 융합 능력까지 포괄한 컴퓨팅 기반의 제반 활동 역량으로 넓게 설정하고 있는 것이다. 디지털 리터러시와 정보기술 활용능력을 대비시켰을 때, 이들 역량을 전자에서는 컴퓨팅 기반의 융합ㆍ통찰에 요구되는 기초 역량으로, 후자에서는 정보 문화 소양의 하위 역량 중 하나로 다루고 있다. <Table 7>은 후자의 정보윤리의식이나 정보보호능력을 인문학적ㆍ심미적 가치 추구 및 향유 차원의 역량으로 간주하여 전자의 심미적 감수성과 대비시켜 제시하고 있다. 여기서 한 가지 주목할 사항은 전자의 역량 중 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량인 데이터 리터러시, 융합ㆍ통찰 역량의 하위 역량인 통찰적 학습 역량, 공감ㆍ혁신 역량의 하위 역량인 성찰ㆍ혁신 역량이 <Table 7>에 명시되어 있지 않다는 점이다. 이는 후자의 역량 연구 당시 초지능ㆍ초융합ㆍ초연결과 관련해 4차 산업혁명 시대가 요구하는 바를 충분한 고찰할 수 없었고, 그로 인해 해당 역량 각각에 대응된 세부 역량을 도출ㆍ제시하지 못했기 때문이다.
Ⅵ. 결론 및 제언
본 연구에서는 4차 산업혁명 교육이 주안점을 두어야 할 핵심 역량을 도출하였다. 이를 위해 4차 산업혁명의 특징을 파악하고 4차 산업혁명 시대에 교육이 어떻게 달라져야 하는지 살펴보았다. 또한, 2015 개정교육과정 핵심 역량을 고찰하고 4차 산업혁명 관련 전문가들이 제시하는 핵심 역량을 분석하였다. 이를 바탕으로 3대 핵심 역량을 도출하였고 핵심 역량별로 3개의 하위 역량을 제시하였다.
도출한 핵심 역량과 하위 역량에 대해 교수, 교사 등 4차 산업혁명 교육 관련 전문가 20여 명의 의견을 수렴하였다. 그 결과, 문제해결 역량의 경우 그 범위가 상위 핵심 역량보다 넓게 해석될 수 있는 측면이 있다거나, 역량 간에 중첩되는 부분이 몇몇 있다는 의견이 일부 있었다.
핵심 역량 및 하위 역량에 대한 전문가의 의견 등 여러 단계의 심층 논의를 통해 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량으로 설정했던 문제해결 역량을 데이터 리터러시 역량으로 변경하였다. 또한, 핵심 역량과 하위 역량의 명칭 일부를 수정하고 각 역량에 대한 정의를 더욱 분명하게 하여 역량의 범위를 명확히 설정하고 역량 간 겹침을 최소화하였다.
최종 확정된 3대 핵심 역량과 그 하위 역량들은 다음과 같다. 3대 핵심 역량은 지능 정보 역량, 융합ㆍ통찰 역량, 공감ㆍ혁신 역량이다. 지능 정보 역량의 하위 역량으로는 컴퓨팅 사고력, 프로그래밍 역량, 데이터 리터러시를, 융합ㆍ통찰 역량의 하위 역량으로는 통찰적 학습 역량, SWㆍAI 융합 역량, 디지털 리터러시를 제시했다. 공감ㆍ혁신 역량의 하위 역량으로는 공존ㆍ공감 역량, 심미적 감수성, 성찰·혁신 역량을 제시했다.
이 연구에서 제안한 ‘4차 산업혁명 교육을 위한 핵심 역량’은 인공지능과 사물인터넷, 메타버스 등 새로운 기술이 초래하는 4차 산업혁명으로 거대한 사회적 변화(mega trend)가 가속화되고 있는 상황에서, 새로운 교육 정책의 설계와 실제 교육 프로그램의 실행에 곤경을 느끼는 일선 교육 현장에 의미 있게 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대한다. 교육의 효과를 위해서는 적절한 교육 방향 설정이 중요하고 우선시 되어야 하는데, 급변하는 기술적ㆍ사회적 환경에서는 이를 파악하여 어떤 인재상을 위해 어떻게 교육해야 할 것인지 새로운 교육적 목표를 수립하기 어렵기 때문이다.
관련 연구로서 본 연구에서 도출한 핵심 역량을 바탕으로 교육과정을 어떻게 운영하는 것이 효율적인지 실제적인 교육 정책의 수립과 수행 측면에서 연구할 필요가 있다. 더 나아가, 현직 교원 또는 예비 교원이 갖추어야 할 4차 산업혁명 교육 관련 핵심 역량이 무엇인지에 대한 연구가 요구된다.
References
- Klaus S. et al, The impact of the 4th industrial revolution, HulRum Press, 2016.
- Ministry of Education, General Overview of Primary / Secondary Curriculum, Ministry of Education Notice 2015-74, Separate book 1, 2015.
- Ministry of Education, Practical (technical family) / Information Subject Curriculum, Ministry of Education Notice 2015-74, Separate book 10, 2015.
- Ministry of Education, A future-oriented curriculum promotion plan with the public (draft), Curriculum Policy Division, 2021.
- H. Kim, et al, A study on restructuring of information subject curriculum and improvement of teaching and learning methods. Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science & Creativity, 2021.
- World Economic Forum, New vision for education: unlocking the potential of technology, 2015.
-
K. Lee, “Exploring Educational Tasks through the Analysis of Talents in the Era of the 4th Industrial Revolution,” The Korea Educational Review, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 143-166, June 2019.
[https://doi.org/10.29318/KER.25.2.6]

-
B. Kim, H. Kwon, and M. Kim, “A Study on the Improvement of Educational System to Strengthen Digital Citizenship in the Age of Artificial Intelligence”, The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 17-25, May 2021.
[https://doi.org/10.32431/kace.2021.24.3.007]

- M. Lee, Exploration of the early-childhood education direction to promote key competencies in the fourth industrial revolution era, Master's Thesis, Graduate School of Education, Dongguk University, 2018.
-
E. Oh and Y. Kim, “The Core Competencies of young children and the Direction of Early Childhood Education in the Fourth Industrial Revolution,” Journal of Digital Contents Society, Vol. 20, No. 5, pp. 1011-1021, May 2019.
[https://doi.org/10.9728/dcs.2019.20.5.1011]

- M. Jang, Roles and functions and students’ core competencies of technical college required in fourth industrial revolution ages, Doctor's Dissertation, Graduate School of Korea National University of Education, 2021.
-
K. Lee and H. Park, “Effects of Learning Support Extracurricular Program on Core Competencies Linked Computational Thinking Course”, The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 37-46. May 2021.
[https://doi.org/10.32431/kace.2021.24.5.004]

- H. Park, Derivation of teacher competency for artificial intelligence convergence education, Master's Thesis, Graduate School of Education, Korea University. 2021.
-
H. Park, J. Kim, & W. Lee, “Derivation of Teachers’ Competency for Artificial Intelligence Convergence Education”, The Journal of Korean Association of Computer Education, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 17-25, Sep 2021.
[https://doi.org/10.32431/kace.2021.24.5.002]

- H. Kang, A Study on the core competencies of the french compulsory curriculum, Master's Thesis, Graduate School of Education, Korea National University of Education, 2018.
-
H. Choe, “Analysis of 2015 Middle School Informatics Curriculum by Viewpoint of Core Competence”, Journal of The Korea Society of Computer and Information, Vol. 21, No. 10, pp. 183-190, Oct 2016.
[https://doi.org/10.9708/jksci.2016.21.10.183]

저자소개

1988년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학사)
1990년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학석사)
1996년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학박사)
2020년~현 재: 제주대학교 교육대학원 인공지능융합교육전공 교수
1997년~현 재: 제주대학교 컴퓨터교육과 교수
※관심분야 : 운영체제, SW 및 컴퓨팅사고력 교육, 컴퓨터교육 등

2005년 : 고려대학교 컴퓨터교육과 (이학사)
2007년 : 고려대학교 컴퓨터교육과 (이학석사)
2017년 : 서울대학교 의료경영과정보학 (공학박사)
2018년~현 재: 제주대학교 경영정보학과 교수
2010년~2018년: 서울대학교 의생명지식공학연구실 연구원
※관심분야 : 지식그래프, 분산/병렬 컴퓨팅, SW·AI 교육 등

2008년 : 서강대학교 국어국문학, 신문방송학 (문학사)
2010년 : 서강대학교 국어국문학 (문학석사)
2015년 : 서강대학교 국어국문학 (문학박사)
2020년~현 재: 제주대학교 교육대학원 인공지능융합교육전공 교수
2016년~현 재: 제주대학교 국어교육과 교수
※관심분야 : AI 교육, AI와 문학, 디지털 인문학, SF 등

2020년 : 제주대학교 컴퓨터교육과 (학사)
2022년 : 제주대학교 융합교육소프트웨어학과 (석사)
2022년~현 재: 제주대학교 과학교육학부 컴퓨터교육전공 박사과정
※관심분야 : SW·AI 교육, 에듀테크, 컴퓨터교육

1989년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학사)
1991년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학석사)
1995년 : 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학박사)
2020년~현 재: 제주대학교 교육대학원 인공지능융합교육전공 교수
1996년~현 재: 제주대학교 컴퓨터교육과 교수
※관심분야 : 컴퓨터시스템, SW·AI 교육, 컴퓨터교육 등