기업의 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량이 서비스 혁신 행동에 미치는 영향 연구
Copyright ⓒ 2021 The Digital Contents Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-CommercialLicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

초록
본 연구는 기업의 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량의 활용과 탐색이 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량이 서비스 혁신행동에 영향을 미치는 과정에서 어떠한 매개역할을 하는지를 알아보고자 함에 있다. 선행연구를 토대로 요인별 측정항목 도출과 연구모형, 그리고 설문 조사를 통한 분석방법을 진행하였다. 분석결과는 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량은 서비스혁신행동과 디지털트랜스포메이션 활용과 탐색에, 그리고 디지털트랜스포메이션 활용과 탐색이 서비스 혁신행동에 영향을 미치고 있음을 보여주었다. 또한 디지털트랜스포메이션 활용과 탐색은 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량이 서비스혁신행동에 영향을 미침에 있어 부분 매개역할을 하였다. 이러한 결과는 기업의 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량, 활용과 탐색, 그리고 서비스혁신행동을 위한 지속적인 노력의 필요성에 대한1 함의와 고객과의 관계가 유지되도록 해야 함을 시사한다. 본 연구결과는 기업의 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량 강화와 활용을 위한 참고자료가 될 것이다.
Abstract
This study aims to find out how the utilization and exploration of a company's digital transformation capabilities play a role as a medium in the process in which digital transformation capabilities affect service innovation behaviors. Based on prior research, the analysis method was carried out through the derivation of measurement items by factor, research model, and survey. Analysis results showed that digital transformation capabilities affect service innovation behaviors, utilization and exploration of digital transformation, and utilization and exploration of digital transformation. Furthermore, digital transformation utilization and exploration played a partial role in the impact of digital transformation capabilities on service innovation behavior. These results suggest that 1 implications of an entity's digital transformation capabilities, utilization and exploration, and the need for continuous efforts to act on service innovation should be maintained and that relationships with the customer should be maintained. The results of this study will be a reference material for companies to strengthen and utilize their digital transformation capabilities.
Keywords:
Digital transformation, Capabilities, Utilization, Exploration, Service innovation키워드:
디지털트랜스포메이션, 역량, 활용, 탐색, 서비스 혁신Ⅰ. 서 론
4차 산업혁명 시대로 진입하면서 ICT 기술 발전과 산업 간의 융복합이 발생하면서 기존의 비즈니스 모델이론을 변화 발전시키는 디지털 트랜스포메이션(Digital Transformation)이 나타났다[8]. 대부분 기업들은 디지털 트랜스포메이션 역량 강화를 위해 거시적 및 다차원적 관점보다는 인공지능(AI), 블록체인, 빅데이터, 사물인터넷(IoT)등과 같은 새로운 기술만을 도입 적용하고자 하였다[6],[5]. 성공적 디지털 트랜스포메이션 역량 강화를 위해서도 완전한 기술은 없다는 인식과 시행착오 과정에서 나타난 문제들의 빠른 수정과 실천 과정의 반복에서 적용 대상 및 범위를 분명하게 구체화하였다 [2]. 서비스 혁신은 신(新)정책과 서비스, 그리고 변화된 프로세스 등의 제공이나 새로운 시장모습을 통해 나타나는데 기업들은 시장에서의 생존을 위해서는 지속적으로 고객과 관계가 이어질 수 있도록 해야 한다 [10].
따라서 본 연구는 기업의 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량의 활용과 탐색이 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량이 서비스 혁신행동에 영향을 미치는 과정에서 어떠한 매개역할을 하는지를 알아보고자 함에 있다. 따라서 선행연구를 토대로 요인별 측정항목 도출과 연구모형, 그리고 설문 조사를 통한 분석방법을 진행하였다.
Ⅱ. 이론적 배경
2-1 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 역량
기업의 디지털 트랜스포메이션 역량은 새로운 디지털 기술을 적용하여 비즈니스모델의 혁신의 변화 및 성과 창출을 통한 기업의 조직과 기술역량을 강화하는 것이다[16],[9]는 성공적 프레임워크에 대한 6가지 관점(전략적 비전, 혁신의 문화, 노하우와 지적 재산, 디지털 역량, 전략적 정렬, 기술 자산)을 분석하였다. [14]은 5단계 전략(디지털 전략 정의, 운영 백본을 위한 투자 행동, 디지털 서비스 플랫폼 설계, 파트너와의 디지털 서비스 플랫폼설계, 서비스 문화)과 디지털 서비스 플랫폼과 운영 백본 중심의 플랫폼 구성을 제시하였다. [1]는 국내외에서 추진 중인 제조 디지털트랜스포메이션과 유관한 정부정책 소개와 동향분석을 통해 인공지능과 데이터사이언스를 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 핵심기술로 제안하였다. [7]은 디지털 기술역량을 활용하여 시장 재편기업들의 전략적 특성으로서 비전, 플랫폼, 개방적 혁신임을 제시하였다.
2-2 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 활용과 탐색
기업적 관점에서 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 활용과 탐색은 새로운 환경변화에 적응 및 대응하는 전략적 운영과정에서 필요한 활동이다. 다양한 분야에서 많은 연구자들이 유사한 개념을 제시했지만 기존의 확실성 활용[12]과 새로운 가능성의 탐색적[17]관점에서 함의로 요약된다. 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 활용과 탐색에 대한 판단기준은 기업의 역량과 자원 그리고 프로세스를 고려해야 되어야 하는데 어떤 기업의 탐색적 활동이 타 기업에서는 활용적 활동이 될 수 있기 때문이다[4]. 기업들의 이러한 노력 속에서 디지털 트랜스포메이션의 활용과 탐색을 위해 함께 조화하는 것을 생존 및 성공을 위한 핵심동인으로 간주하면서[11] 다양한 연구들을 시도하고 있다.
2-3 서비스 혁신 행동
혁신은 새롭게 개발된 아이디어 방식으로 개발되면서 개인이나 조직의 업무부분에 적용 또는 필요 제품개발과 서비스로서 발전되게 하는 작업공정의 개념의 의미를 함의하고 도출된 아이디어의 실천과 적용, 최종적으로 확산까지 모두 포함하는 개념이다[3],[15]도 서비스 혁신과 관련하여 급진적이고 점진적 서비스 혁신이 가장 보편적 범주라 하였지만 두 관점의 차이는 분명하지는 않다고 하였다. 특히 급진적 서비스 혁신에서의 참신성도 새로운 서비스와 기존 서비스의 구성, 변화된 프로세스, 새로운 정책 등이 포함될 수도 있지만 시장에서 새로운 모습과정에서 분명해질 수도 있다[10]. 동일한 관점에서 [13]은 기업이 제공하는 현재 서비스와는 큰 차이점이 있으며 역량 적용이 요구되는 큰 변화가 필요하다고 하였다.
Ⅲ. 연구 방법
3-1 연구 모형과 연구가설
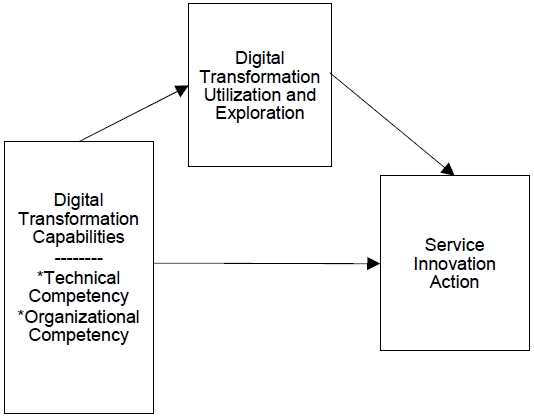
본 연구의 연구모형은 <그림 1>과 같고 연구가설을 설정하였다.
연구가설1. 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량은 서비스혁신 행동에 영향을 미칠 것이다.
연구가설2. 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량은 디지털트랜스포메이션 활용과 탐색에 영향을 미칠 것이다.
연구가설3. 디지털트랜스포메이션 활용과 탐색은 서비스혁신행동에 영향을 미칠 것이다.
연구가설4. 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량이 서비스혁신행동에 영향을 미침에 있어 매개역할을 활 것이다.
3-2 연구 대상자
본 연구에서는 설문지를 250부 배포하여, 본 연구와 부합하지 않거나 회수할 수 없는 설문지를 제외하고 207부만을 연구 자료로 활용하였다. 설문지에 응답한 사람들의 일반적 특성은 다음과 같다.
3-3 측정 도구
디지털트랜스포메이션 역량연구에 사용된 변수들에 대한 개념타당도를 분석하기 위해 탐색적 요인분석결과 3개 요인이 추출되었고, 각 요인들로서 구성된 항목들 사이에는 타당성 있었다<표3-3>. 요인분석에 대한 적합성을 분석하는 KMO(Kaiser -Mayer-Olkin)값이 .964로 나타나 요인분석에 사용된 변수들의 선정이 양호하다고 진단할 수 있다.
연구에서 사용 변수들이 특정개념을 균일하게 설명하는가를 검토하기 위해 Cronba ch's ɑ 신뢰도검정 분석결과 Cronbach's ɑ값이 .891∼.966으로 나타나 본 연구에 사용된 변수들은 항목 간 내적 일관성이 있음을 알 수 있다.
본 자료의 통계 분석을 위해서 Spss Windows 21.0을 사용 통계 처리하였다. 이 과정에서 빈도 분석(Frequency Analysis), 주성분 분석, 직각 회전 방식의 요인 분석, 크론바하 알파테스트 (Cronbach alpha test)를 사용 분석하였다. 또한 기술통계(Descriptive analysis), 상관관계분석(Correlation analysis)과 회귀분석(Regre ssion Anal ysis), 독립표본 t-test 분석, 분산분석(oneway ANOVA)을 이용하였다. 수집된 자료의 통계적인 유의수준을 검정하기 위하여 유의 수준은 α =.05로 하였다.
Ⅳ. 연구 결과
4-1 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량 연구개념 기술통계
디지털트랜스포메이션 역량 연구변수들의 상관구조를 살펴보면<표4-1> 모든 변수 간의 상관크기가 나타나 99% 신뢰수준에서 통계적으로 유의한 강한 상관관계가 있다고 해석할 수 있다.
4-2 연구개념들 사이의 상관관계 분석
디지털트랜스포메이션 역량 연구변수들의 상관구조를 살펴보면<표4-2> 모든 변수 간의 상관크기를 보였는데, 99% 신뢰수준에서 통계적 유의한 강한 상관관계가 있다고 볼 수 있다.
4-3 연구가설 검증
연구가설 1을 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 회귀식은(R²=.560, F=129.956, p<.001)로 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적으로 유의한 영향관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 독립변수별로도 95% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적인 유의한 영향을 미치고 있음을 보여주었다. 따라서 연구가설 1은 채택되었다.
연구가설 2-1. 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 회귀식은 (R²=.864, F=648.364, p<.001)로 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적으로 유의한 영향관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 독립변수별로도 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적 유의한 영향을 미치고 있음을 보여주었다. 따라서 연구가설 2-1은 채택되었다.

The effect of digital transformation organizational competency and digital transformation technology capability on digital transformation technology capability utilization and exploration-Multiple regression analysis
연구가설 2-2. 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 회귀식은 (R²=.809, F=432.923, p< .001)로 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적으로 유의한 영향관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 독립변수별로도 95% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적으로 유의한 영향을 미치고 있다. 연구가설 2-2는 채택되었다.
연구가설 3. 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 회귀식은 (R²=.604, F=155.680, p<.001)로 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적으로 유의한 영향관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 독립변수별로도 99.9% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적인 유의한 영향을 미치고 있음을 보여주었다. 따라서 연구가설 3은 채택되었다.
연구가설 4-1. 매개효과를 분석하기 위해 위계적 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 회귀식은 (R²=.590, F=97.345, p<.00 1)로 95% 신뢰수준에서 통계적 유의한 영향관계가 있음을 보여주었다. 독립변수별로도 95% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적인 유의한 영향을 미치고 있음을 보였다. 매개변수의 투입으로 설명력이 3.0% 향상되었고, 매개효과유형에서는 부분매개효과가 있음을 보여주었다. 따라서 가설 4-1은 채택되었다.

The effect of digital transformation organizational competency and digital transformation technology competency on service innovation behavior-hierarchical multiple regression analysis
연구가설 4-2. 매개효과를 분석하기 위해 위계적 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과 1단계에서 디지털트랜스포메이션 조직역량, 디지털트랜스포메이션 기술역량을 독립변인으로 하고 서비스 혁신행동을 종속변인으로 한 회귀식은 (R²=.601, F=102.004, p<.001)로 95% 신뢰수준의 통계적 유의한 영향관계가 있음을 보여주었다. 독립변수별로도 95% 신뢰수준 이상에서 통계적 유의한 영향을 미치고 있다. 매개변수의 투입되므로 설명력이 4.1% 향상되었고, 매개효과유형에서는 부분매개효과가 있음을 보여주었다. 가설 4-2는 채택되었다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
본 연구의 분석결과를 종합하면 서비스 영업중심시대에서 디지털플랫폼을 통해 업무 처리 가능시대로 변화하고 고객과의 접점도 플랫폼이 되어 가고 있다. 따라서 플랫폼의 정기적 업데이트를 통하여 고객의 니즈를 위한 새로운 서비스를 실행과 개선 작업의 진행을 통해 기업의 디지털플랫폼 역량을 강화 할 필요성이 있다. 특히 고객과 마주하는 현장에서 서비스혁신행동의 발휘가 가능하다면 고객입장에서 경험하는 만족도 역시 높아질 가능성이 있다.
본 연구는 기업의 상황에 따라 다양한 차이가 발생될 수 있음을 간과하고 있어 설문응답자의 응답도 일정한 한계가 있다. 시사점으로는 디지털트랜스포메이션 역량 향상에서 요구되는 다양한 영역지표를 만들어 IT 기술적 관점이 아니라, 기업조직문화, 대 고객 서비스 등을 위한 통합적 관점에서 대응 전략을 마련할 필요가 있다.
References
- J. W. Kwon, T. S. Song(2019), “Platform-based digital transformation trend for manufacturing innovation”, 『The Institute of Electronics and Information Engineers,The Magazine of the IEEE』, 46(12): 34-46.
-
S.Y.Kim, J. J. Ma , "A study on the digital transformation strategy of a fashion brand - Focused on the Burberry case",2019, vol.27, no.5, pp. 449-460
[https://doi.org/10.29049/rjcc.2019.27.5.449]

-
J.K. Kim (2017), “The Effect of Emotional Intelligence on Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Innovative Behavior in Manufacture of Automobile industry”, 2017 Journal of Digital Convergence, 15(2): 80.
[https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2017.15.2.67]

-
H.j. Kim, N.K Park(2010). “The Conceptual Definition and Future Study Plan for Exploration and Exploitation Studies”, Journal of Strategic Management』, 13(3): 1-34.
[https://doi.org/10.17786/jsm.2010.13.3.001]

- W.H Lee(2019), “A Study on Digital Transformation as A Business Strategy: Building a Total Digital Business Strategy Framework for Distribution”, Journal of Distribution and Management Research』, 22(3): 85-99.
- J. K lee(2018), “Trends and Implications for Advanced Companies’ Digital Transformation: Need to Build a Business Model in the Age of the 4th Industrial Revolution”, 『Hyundai Research Institure』, 810: 1-20.
- H.G Lee, S.Y Lee (2020), “Creative Industry Digital Transformation Case Study : Market Reorganization Strategy and Platform”, 『Journal of Digital Convergence』, 18(7): 177-188.
- S.W Hong, Y.H Choi ,G.Y Gim(2019), “A Study of Development of Digital Transformation Capacity”, 『The Korea Society of Information Technology Policy & Management』, 11(5): 1371-1381.
-
Gurbaxani, V., & Dunkle, D. (2019), “Gearing Up For Successful Digital Transf ormation”, MIS Quarterly Executive, 18(3).
[https://doi.org/10.17705/2msqe.00017]

-
Harris R., McAdam R., McCausland I. & Reid R.(2013), “Levels of innovation wi thin SMEs in perpeal regions : the role of business improvement initiatives”, 『Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development』,20(1), 102-124.
[https://doi.org/10.1108/14626001311298439]

-
Jansen J. J., Simsek Z. & Cao Q.(2012), “Ambidexterity and performance in mu ltiunit contexts: Cross‐level moderating effects of structural and resource attributes ”, 『Strategic Manage Journal』, 33(11), 1286-1303.
[https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.1977]

-
March J. G.(1991). “Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning”, 『Organization science』, 2(1), 71-87.
[https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2.1.71]

-
Ordanini A. & Parasuraman. A.(2011), “Service innovation viewed through a service-dominant logic lens: a conceptual framework and empirical analysis”, 『Journal of Service Research』, 14(1), 3-23.
[https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670510385332]

- Sebastian, I., Ross, J., Beath, C., Mocker, M., Moloney, K., & Fonstad, N.(2017), “How big old companies navigate digital transformation”, 『MIS Quart erly Executive』,16(3): 197-213.
-
Snyder H., Witell L., Ustafsson A.. Fombelle P. & Kristensson P.(2016). “Identi fying categories of service innovation: A review and synthesis of the literature”, 『Journal of Business Research』, 69(7):2401-2408.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.01.009]

- Westerman, G., Calmejane, C., Bonnet, D. Ferraris, P., & McAfee, A.(2011), “Digital Transformation: A roadmap for billion-dollar organizations”, 『MIT Center for Digital Business and Capgemini Consulting』, 1:1-68.
-
He, Z. and P. Wong (2004), “Exploration vs. exploitation: An empirical test of the ambidexterity hypothesis”, Organization Science, 15(4): 481-494
[https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1040.0078]

저자소개

2008년 : 군산대학교 정보통신학과 (공학학사)
2010년 : 중앙대학교 대학원 (공학석사)
2010년~2016년: CJ 올리브네트웍스
2016년~현 재: 화웨이 코리아
2018년~현 재: 서울과학종합대학원 경영학 박사과정
※관심분야:디지털트랜스포메이션, 클라우드 컴퓨팅, 서버리스 컴퓨팅 등

2005년 : 중앙대학교 컴퓨터공학과 (공학학사)
2007년 : 중앙대학교 대학원 (공학석사)
2010년 : 중앙대학교 대학원 (공학박사)
2012년~2017년: 한국과학기술정보연구원(KISTI)
2017년~현 재: 중앙대학교 소프트웨어학부 교수
※관심분야:디지털트랜스포메이션, 클라우드 컴퓨팅, 대용량 데이터 시스템

1998년 : 건국대학교 축산경영학과 (경영학사)
2016년 : Aalto 대학교 (경영학석사)
2020년 : 서울과학종합대학원 (경영학박사)
2020년~현 재: ㈜세일즈스쿨앤컴퍼니
2020년~현 재: 산업정책연구원 연구교수
2020년~현 재: 서울과학종합대학원 경영학과 교수
※관심분야:과학적 영업, 영업역량, 신뢰 자본 등